What Is a Dental Implant?
A dental implant is a surgical component that replaces the root of a missing tooth. It is typically made from titanium and is placed into the jawbone, where it integrates with the bone over time. Once the implant has successfully fused with the bone, a crown is placed on top to mimic the appearance and function of a natural tooth. This process not only restores the smile but also helps maintain bone structure and facial integrity. Dental implants have become a well-regarded option for individuals who have lost one or more teeth due to injury, decay, or periodontal disease.
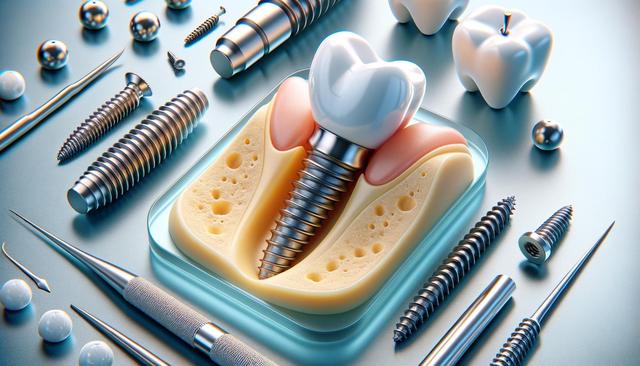
The structure of a dental implant consists of three main parts:
- The implant post – acts as the tooth root and is anchored into the jawbone.
- The abutment – a connector that holds the crown in place.
- The crown – the visible part of the implant that resembles a natural tooth.
This combination makes dental implants a stable and long-lasting solution when compared to traditional dentures or bridges.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Dental Implants?
Not everyone is an immediate candidate for dental implants. Several factors determine whether a person is suitable for this procedure. Good oral and general health are essential, as the success of dental implants depends on the body’s ability to heal and support the implant. One of the key requirements is sufficient bone density in the jaw to hold the implant securely. If bone loss has already occurred, a bone graft may be recommended to rebuild the area before implant placement.
Ideal candidates for dental implants typically:
- Have one or more missing teeth
- Have healthy gums and sufficient jawbone structure
- Do not have medical conditions that would interfere with bone healing
- Are non-smokers or willing to quit smoking during the healing process
A thorough dental evaluation, including X-rays and sometimes 3D scans, is necessary to determine candidacy. The dentist will also review medical history and discuss lifestyle habits that may impact healing and implant success.
The Procedure and Healing Process
The process of getting a dental implant usually involves multiple stages, spread over several months. Initially, the implant is surgically placed into the jawbone under local anesthesia. This is followed by a healing period known as osseointegration, where the bone grows around the implant, securing it in place. This phase can take several weeks to a few months, depending on the individual’s healing ability and the complexity of the case.
After successful osseointegration, the abutment is attached, and a custom-made crown is placed on top. Throughout the process, temporary restorations may be used to maintain aesthetics and function. The final result is a stable, natural-looking tooth replacement that blends seamlessly with the surrounding teeth.
During the healing stages, patients are advised to:
- Follow a soft food diet to avoid disturbing the implant site
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene to prevent infection
- Attend follow-up appointments for monitoring progress
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption
These steps greatly improve the chances of long-term implant success and reduce complications.
Benefits of Choosing Dental Implants
Dental implants offer several advantages over other tooth replacement options. One of the most significant benefits is their ability to preserve jawbone structure. When a tooth is lost, the underlying bone begins to deteriorate over time. Implants stimulate the bone similarly to natural tooth roots, helping prevent bone loss. They also provide a fixed solution that does not shift or slip, unlike removable dentures.
Other notable benefits include:
- Improved speech and comfort
- Enhanced chewing efficiency and taste sensation
- Long-term durability with proper care
- Natural appearance and feel
Additionally, dental implants do not require the alteration of adjacent teeth, as is common with bridges. This preservation of natural tooth structure contributes to better long-term oral health. With consistent oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups, implants can serve patients well for many years.
Maintenance and Long-Term Care
Maintaining dental implants is similar to caring for natural teeth. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups are essential to ensure their longevity. While implants are resistant to decay, the surrounding gum tissue and bone must remain healthy to support the implant over time. Neglecting oral hygiene can lead to peri-implantitis, a condition similar to gum disease that can compromise implant stability.
To care for dental implants effectively, patients should:
- Brush at least twice daily with a non-abrasive toothpaste
- Floss or use interdental brushes to clean around the implant
- Use an antimicrobial mouth rinse if recommended by the dentist
- Visit the dentist every six months for professional cleaning and examination
In some cases, custom tools or techniques may be suggested for those with multiple implants or limited dexterity. Dental professionals can provide tailored advice to help patients maintain their implants and overall oral health.



Leave a Reply